When do the initial pregnancy symptoms emerge?
If you’re a woman in your childbearing years attempting to conceive, or if you’ve engaged in unprotected intercourse and are now concerned about the possibility of an unplanned pregnancy, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the early indicators of pregnancy.
These early pregnancy signs can often be overlooked or mistaken for symptoms of an illness or premenstrual syndrome. Identifying pregnancy symptoms is crucial for maintaining a healthy pregnancy and making suitable prenatal preparations.
Contrary to common misconceptions, there are no pregnancy symptoms immediately following fertilization. The first signs only become apparent when the embryo implants in the uterus, typically one to two weeks after intercourse.
From the moment the embryo implants in the uterus until around the 13th week of pregnancy, a pregnant woman’s body undergoes various transformations, accompanied by a significant increase in hormone production.
Many of these changes lead to noticeable symptoms. Most of these symptoms begin to appear around the 5th or 6th week of pregnancy, which is approximately 2 to 3 weeks after the intercourse that resulted in the pregnancy (pregnancy duration is calculated from the date of the last menstrual period).
At the end of this article, we provide two calculators for you to estimate the likelihood of being pregnant and how far along you may be in your pregnancy if you are indeed expecting.
What are the first symptoms of pregnancy?
Listed chronologically, the early signs and symptoms of pregnancy typically include:
- Light vaginal bleeding (does not occur in most cases).
- Missed period (always occurs).
- Abdominal cramps.
- Breast tenderness.
- Increased breast size.
- Changes in breast appearance.
- Nausea.
- Excessive salivation.
- Constipation.
- Bloating.
- Fatigue and sleepiness.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Food cravings.
- Changes in taste and smell.
- Intolerance to strong odors.
- Increased intestinal gas.
- Dizziness.
- Mood swings.
- Headaches.
- Vaginal discharge.
- Acne.
- Pregnancy rhinitis.
- Leg cramps.
- Hemorrhoids.
- Postural hypotension.
Vaginal Bleeding
- Frequency: Uncommon.
- When it occurs: Between the 3rd and 4th week of pregnancy.
The first pregnancy sign is often subtle vaginal bleeding. Not all women experience this sign, and some who do may not recognize it as a pregnancy symptom.
When the egg is fertilized, it transforms into a zygote (the embryo’s earliest developmental stage) and begins its journey through the fallopian tube towards the uterus. After 6 to 12 days, the embryo reaches the uterus and implants itself in the uterine wall, a process called implantation or nidation. This implantation can cause minor uterine bleeding, manifesting as slight vaginal bleeding.
What is the embryo implantation bleeding like?
Since implantation bleeding can last up to three days, cause mild abdominal cramps, and occur close to the expected menstruation time, some women interpret it as a light period and do not suspect it is their first pregnancy sign.
In most cases, however, implantation bleeding is quite subtle, ranging from a dark red to a slightly pink and thin discharge.
So, if you’re trying to conceive and experience unusual menstruation or discharge, pay attention, as it could be an early pregnancy sign.
Is it normal to have bleeding in early pregnancy?
The only vaginal bleeding considered normal in early pregnancy is the bleeding that occurs during the embryo’s implantation in the uterus. However, this bleeding usually appears before a woman knows she is pregnant.
It’s important to note that the embryo’s implantation in the uterus is just one of several causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. Over 20% of pregnant women experience some bleeding in the first trimester.
Any bleeding that occurs after a pregnant woman already knows she is expecting should be reported to the obstetrician.
Missed Period
- Frequency: Occurs in 100% of cases.
- When it occurs: Around the 4th week.
Since implantation bleeding is relatively uncommon, in practice, the first pregnancy symptom for most women ends up being a missed period. This is the sign that typically prompts women to take a pregnancy test.
Do all pregnant women experience a missed period?
Yes, this sign is universal for all pregnant women. Those who are pregnant do not menstruate, and those who menstruate cannot be pregnant. To better understand this relationship, please read: Can You Have Your Period While Pregnant?
Keep in mind, though, that not all women can quickly notice a missed period. Some women have very irregular menstrual cycles and go through times when they don’t ovulate in a specific month. This can make the gap between their periods longer than one or even two months.
Additionally, as explained earlier, episodes of vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy can mimic menstruation, delaying the realization that the woman is no longer menstruating.
Can a period be late and not be due to pregnancy?
Yes, a period can be late for various reasons apart from pregnancy, including stress, infections, changes in contraceptives, weight fluctuations, fatigue, etc.
The anticipation of menstruation, especially when a woman does not want to become pregnant but engaged in unprotected intercourse, can also cause a delayed period.
If your period is late, and you are unsure of the cause, read on: Why is my period late? 15 reasons besides pregnancy.
How many days after a missed period can I take a pregnancy test?
Current over-the-counter and blood pregnancy tests can detect an ongoing pregnancy after the first day of a missed period.
Cramps or Abdominal Pain
- Frequency: Common.
- When it occurs: Between the 4th and 5th week.
Early pregnancy can cause not only light bleeding but also some discomfort in the lower abdomen or a feeling of abdominal bloating, much like premenstrual symptoms.
These discomforts and cramps, when accompanied by vaginal bleeding, can easily deceive pregnant women, making them think they have menstruated.
Is it normal to have cramps during pregnancy?
Yes, it’s perfectly normal, and even expected to experience cramps during pregnancy. In the first trimester, the pain usually comes from the uterus starting to grow and hormonal changes.
Abdominal pain is a symptom that can appear in the first, second, or third trimester of pregnancy. In the first few weeks of pregnancy, it may feel more like a sensation of weight or discomfort rather than an actual cramp.
We talk specifically about the causes of abdominal pain in pregnancy in the following article: Main causes of abdominal pain in pregnant women.
Breast Pain
- Frequency: Very common.
- When it occurs: Around the 5th week.
Another typical pregnancy sign, increased breast sensitivity, can appear early, just two or three weeks after fertilization. Often, the simple act of touching the breasts or putting on a bra can be very uncomfortable.
For women who don’t experience implantation bleeding and haven’t identified a missed period, breast tenderness can be the first noticeable pregnancy symptom.
To find out about the main causes of breast pain, take a look at this article: Breast Pain: Causes, Treatment and the Risk of Cancer.
Breast enlargement
- Frequency: very common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th week.
In addition to sensitivity, pregnant women’s breasts also tend to become larger, causing a sensation of swelling.
This increase in breast size occurs due to hormonal changes that stimulate the development of mammary glands, preparing them for the upcoming breastfeeding period.
The increase in breast volume usually appears one to two weeks after the pregnant woman notices that they are more sensitive.
Changes in breast appearance
- Frequency: very common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
Besides breast tenderness and enlargement, hormones produced during pregnancy cause changes in the appearance of pregnant women’s breasts. Nipples darken, and veins appear around the breasts. These changes persist during the breastfeeding period.
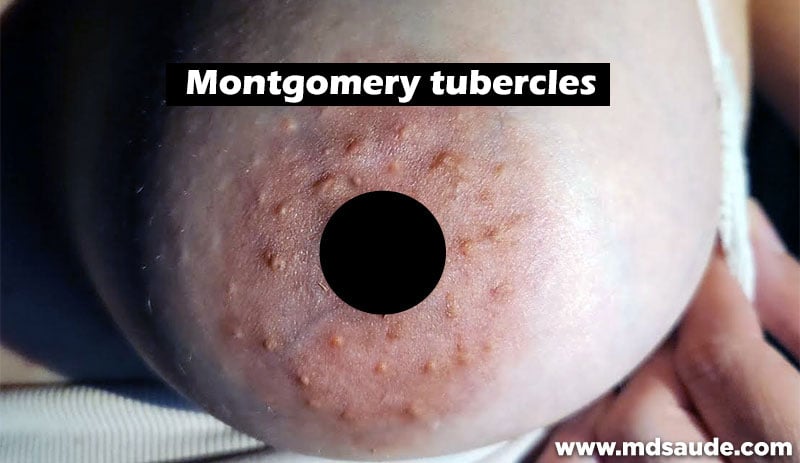
Another noticeable alteration is the appearance of Montgomery tubercles, small nodules located on the areolas. These glands lubricate the areola and nipple, keeping them moisturized. As the breast grows during pregnancy, the tubercles become more visible.
Montgomery tubercles are quite common during pregnancy, but they can also be present in non-pregnant women, especially during puberty and around menstruation.
Nausea and Vomiting
- Frequency: very common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of pregnancy. Up to 70% of pregnant women experience nausea in the first trimester.
In some cases, women are unable to eat due to severe nausea. Severe nausea that requires medical support is part of a condition called hyperemesis gravidarum.
When do pregnancy nausea and vomiting occur?
Nausea usually starts around the 6th week of pregnancy. However, some women may experience these symptoms as early as the 4th or 5th week.
How long does pregnancy nausea last?
Nausea and vomiting are typical symptoms of the first trimester of pregnancy and tend to disappear in the second trimester. Nausea typically improves after the 12th week and resolves by the 18th week for most pregnant women.
Why do pregnant women feel nauseous?
The causes of nausea during pregnancy are not entirely understood. However, this symptom seems to be linked to the production of the hormone hCG, commonly referred to as the pregnancy hormone, which begins to be produced abundantly when the embryo implants in the uterus.
Excessive salivation (Sialorrhea)
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
Along with nausea, pregnant women may also notice an increase in saliva production, called ptyalism, hypersalivation or sialorrhea.
The increase in salivation can occur due to hormonal influence or decreased swallowing of saliva due to nausea.
This symptom can persist until the end of pregnancy in many women, even after nausea subsides.
Constipation
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
The increase in progesterone hormone production during pregnancy causes some organs and tissues in the body to become “looser” or more “relaxed.” This occurs to facilitate the significant expansion of the uterus that is to come.
Among these organs are the intestines, which, due to reduced ability to contract, have more difficulty maintaining normal bowel movements, resulting in constipation.
Bloating
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
Last week, you were confident that you could squeeze into those tight jeans, but now they won’t even close around your belly.
This can happen because, even when the fetus is still too small to expand the uterus, some women experience abdominal bloating that occurs as preparation for the body to withstand uterine growth.
Bloating is another symptom that can be mistaken for premenstrual symptoms.
Fatigue and excessive sleepiness
- Frequency: very common
- When it occurs: around the 5th to 6th week.
A feeling of exhaustion disproportionate to your daily activities is a very common pregnancy symptom. If you already have a tiring routine during the day, it can become overwhelming at the beginning of pregnancy.
Increased sleepiness is also very common. Your body signals that it needs more rest frequently. You may start wanting to go to bed earlier and have more difficulty waking up in the morning. During the day, a good nap seems to be all you desire.
Why do pregnant women feel so sleepy and tired?
Fatigue and sleepiness during pregnancy are due to hormonal changes, primarily progesterone, which directly affects the central nervous, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems.
Fatigue is an early pregnancy symptom that usually disappears in the second trimester. However, it returns in late pregnancy when the baby is already large and heavy.
Frequent urination
- Frequency: very common.
- When it occurs: from the 5th or 6th week.
After about six weeks of pregnancy, the pregnant woman begins to feel the urge to urinate more frequently. These trips to the bathroom may even occur during the night, disturbing sleep.
Why do pregnant women urinate frequently?
In the first few weeks, increased urine occurs due to a reduction in the bladder’s ability to empty completely, due to relaxation caused by pregnancy hormones. In late pregnancy, the large fetus compresses the bladder, reducing its storage capacity and causing even small volumes to trigger the urge to urinate.
Increased urinary frequency is an early pregnancy symptom that occurs in practically 100% of pregnant women and unfortunately lasts until the end of pregnancy.
Note that if increased urinary frequency is accompanied by darker or bloody urine and/or burning sensation during urination, a urinary tract infection may be the cause.
Food cravings
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: from the 6th week.
Craving certain foods in the early weeks of pregnancy is one of the most cliché symptoms of pregnancy. These strange cravings can even make vegetarian women feel like eating hamburgers.
Pregnant women can develop aversions to certain foods and smells as well. That Japanese restaurant you love might cause you nausea just by walking past it while pregnant.
Why do pregnant women have cravings?
We don’t know exactly why pregnancy food cravings occur. They probably arise due to emotional changes and increases in hormones, especially progesterone and hCG.
Why do some pregnant women want to eat strange things, like bricks, ice, or dirt?
The desire to eat non-food substances is called pica. When these strange cravings arise during pregnancy, it can be a sign of micronutrient deficiencies, such as iron, zinc, or selenium.
Taste and smell changes
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 6th week.
In addition to having food cravings and aversions, changes in taste are another very common symptom of pregnancy.
Sweets may become overly sweet, the coffee you love may taste weird, and during the day, you may experience a metallic taste in your mouth for no apparent reason.
Aversion to strong odors
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 6th week.
Just as some foods can cause nausea in the early weeks of pregnancy, strong smells, even pleasant ones, like perfumes or foods, can make you feel sick. Bad or very strong odors, such as cigarette smoke, gasoline, alcohol, cleaning products, etc., have the same effect.
A frequent symptom of pregnancy is an increased sense of smell. Pregnant women often report having developed a heightened sense of smell, where odors that previously went unnoticed or didn’t bother them now become unbearable.
Frequent gas elimination
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 6th week.
Some women experience an increase in intestinal gas in the early weeks of pregnancy. This can be an embarrassing symptom in cases where the pregnant woman needs to be stuck in an office or room with others for hours.
What are the symptoms of gas in pregnancy?
Excess gas in pregnancy usually manifests as an increase in the need to burp and pass flatus (farts), a feeling of bloated abdomen, sensation of gas moving in the intestines, and abdominal cramps.
Dizziness
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: from the 6th week onwards.
Dizziness is another classic pregnancy symptom. Pregnancy hormones cause various changes in a woman’s body, which can lead to dizziness. These changes include a drop in blood pressure, a reduction in blood sugar levels, anemia, increased respiratory rate (which can lead to hyperventilation during physical exertion), insufficient food intake due to nausea, and more.
Mood Swings
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 6th week.
Mood swings are another well-known pregnancy symptom. Pregnant women may cry at small things or have sudden mood changes. They can go from happiness to sadness, or from friendliness to anger quickly. There are cases of pregnant women who even resign from their jobs during bouts of irritation.
Headache
- Frequency: uncommon.
- When it occurs: around the 8th week.
Hormonal changes, blood vessel relaxation, and changes in cerebral blood flow explain why some pregnant women experience headaches during pregnancy. Stress and fatigue also contribute. Headaches are a symptom that usually appears in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Vaginal Discharge
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: around the 8th week.
The appearance of vaginal discharge or an increase in normal discharge are typical symptoms of pregnancy. Frequently, discharge becomes more intense during the second trimester of pregnancy, but some pregnant women notice it from the beginning.
What is normal pregnancy discharge like?
Natural vaginal discharge is stimulated by estrogen and may increase in volume during periods of heightened hormonal stimulation, such as pregnancy. This discharge is typically thick, milky or clear, and odorless.
To read about vaginal discharge, visit: Vaginal Discharge: White, Yellow, Brown, Smelly, Thick…
Acne
- Frequency: uncommon.
- When it occurs: from the 10th week onwards.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause some women to develop acne or experience a worsening of existing acne, due to hormonal imbalances that increase skin oiliness. Acne during pregnancy can range from mild to severe and may occur at any time.
Stuffy Nose – Pregnancy Rhinitis
- Frequency: quite common.
- When it occurs: at any point during pregnancy, but more common from the 13th week onwards.
Pregnancy rhinitis is nasal congestion that starts during pregnancy, lasts for at least six weeks, and is not caused by infection or allergies. It usually resolves within two weeks after giving birth. Pregnancy rhinitis occurs simply because a woman is pregnant, although the exact reason remains unknown.
Between 20 and 30% of pregnant women develop symptomatic nasal congestion during pregnancy. Patients typically experience persistent congestion, accompanied by watery or thick nasal secretions. Sneezing, tearing, and itching in the eyes may also be present. Nasal congestion can lead to mouth breathing at night, reducing sleep quality and exacerbating fatigue and drowsiness during pregnancy.
Leg Cramps
- Frequency: quite common.
- When it occurs: from the 13th week onwards.
Leg cramps are quite common during pregnancy, especially from the middle of the pregnancy onwards.
Cramps are painful muscle contractions, usually felt in the calves or feet at night. The exact causes are unknown, but various factors may be involved, such as changes in maternal circulation, increased leg strain due to weight gain, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.
Hemorrhoids
- Frequency: quite common.
- When they occur: starting from the 13th week, but more prevalent after the 28th week.
Hemorrhoids are enlarged and inflamed veins in the anus and rectum that can cause pain, itching, and anal bleeding.
During pregnancy, hemorrhoids often develop due to increased pressure on rectal veins. This pressure can result from a rise in blood volume circulating in the mother’s veins, the growing weight of the uterus compressing the hemorrhoidal veins, and straining during bowel movements caused by constipation.
Up to 50% of pregnant women develop hemorrhoids during pregnancy. These may be accompanied by symptoms such as anal itching, pain during bowel movements, or rectal bleeding.
Postural hypotension
- Frequency: common.
- When it occurs: starting from the 20th week.
Pregnancy can cause postural hypotension, which is a sudden drop in blood pressure that occurs immediately after standing up from a sitting or lying position (orthostatic hypotension) or after a pregnant woman lies on her back for an extended period (supine hypotension syndrome).
Postural hypotension occurs because the enlarged uterus compresses the inferior vena cava, reducing blood flow returning from the lower extremities to the heart.
With orthostatic hypotension, standing up too quickly can cause dizziness, darkened vision, weakness, a rapid heartbeat, and even fainting.
Is it possible to know if I am pregnant through early symptoms?
Diagnosing pregnancy through symptoms was the norm in the past due to the lack of pregnancy tests and ultrasounds. However, as early signs are nonspecific and only become apparent after several weeks, sometimes even months, of pregnancy, it is neither easy nor practical to diagnose pregnancy this way anymore. Nonetheless, recognizing early symptoms remains crucial.
Identifying early pregnancy signs and symptoms can prompt women to take a pregnancy test, whether over-the-counter or blood tests for hCG. Some women turn to homemade pregnancy tests when they suspect they’re pregnant, but these tests are not only unreliable, they can also be harmful.
The sooner a woman knows she is pregnant, the sooner she can start prenatal care. This enables her to promptly implement beneficial measures for the fetus, such as controlling blood glucose, improving her diet, taking supplements like folic acid and iron, monitoring blood pressure, treating infections promptly, and avoiding alcohol consumption or potentially harmful medications during the first trimester of pregnancy.
It’s important to note that pregnancy symptoms vary among women. Furthermore, a mother may experience entirely different symptoms in her second pregnancy compared to her first. Even when these signs recur, they can differ in intensity, frequency, onset, and duration.
Another point to emphasize is that many early pregnancy symptoms can resemble premenstrual discomforts. It is pretty common for women who are not pregnant to confuse premenstrual symptoms with those of early pregnancy.
Interestingly, the opposite is also true, as many pregnant women don’t pay much attention to early symptoms and only discover they are pregnant towards the end of the first trimester when the signs become too obvious to overlook.
Calculate your probability of being pregnant
Answer the questions below and tally up the points to determine your chances of being pregnant.
- Have you engaged in unprotected sex (without using a condom or other contraceptive methods) within the last 4 weeks?
- Yes (7 points).
- No (-5 points).
- Is your period late?
- No, it’s still 1 week or more away (-1 point).
- No, but it’s due in the next 3 days (0 points).
- Yes, less than 3 days late (1 point).
- Yes, 3 to 6 days late (2 points).
- Yes, more than 7 days late (5 points).
- How many of the following symptoms are you experiencing: nausea, breast pain, breast enlargement, fatigue, frequent sleepiness, frequent urination, bloating, food cravings, mood swings, or abdominal pain?
- None (0 points).
- 1 to 3 symptoms (2 points).
- 4 or more symptoms (4 points).
Results:
- 10 or more points: Very high chance of being pregnant. Consider taking a pregnancy test.
- Between 6 and 9 points: High chance of being pregnant. Consider taking a pregnancy test.
- Between 3 and 5 points: There is a possibility that you are pregnant, but it’s not the most likely outcome.
- Less than 3 points: Low probability of being pregnant.
Pregnancy due date calculator – How many weeks am I?
If you suspect you may be pregnant, use our pregnancy due date calculator to estimate your gestational age (please note: it’s essential to take a test to confirm your pregnancy).
I suspect I am pregnant; what should I do?
If you suspect you might be pregnant, the first step is to take an over-the-counter pregnancy test. However, to minimize the risk of a false-negative result, waiting until you have at least a one-day delay in your menstrual period before taking the test is best. The more days of delay in your menstrual period, the more reliable the pregnancy test result will be.
If the over-the-counter pregnancy test is positive, it’s recommended to confirm the result with a blood test by measuring your hCG levels.
References
- Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of early pregnancy – UpToDate.
- A prospective study of the onset of symptoms of pregnancy – Journal of Clinical Epidemiology.
- Development and validation of a pregnancy symptoms inventory – BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.
- Early Pregnancy Symptoms – WebMD.
- Myth or fact: can women self-diagnose pregnancy? – The Journal of the Medical Society of New Jersey.
- Is this patient pregnant? Can you reliably rule in or rule out early pregnancy by clinical examination? – JAMA.
- Pregnancy Symptoms – Early Signs of Pregnancy – American Pregnancy Association.
- Ptyalism gravidarum – North American journal of medical sciences.
Author(s)







Leave a Comment