What is hCG?
The acronym hCG stands for human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone produced by the cells of an embryo. It is commonly measured in blood tests to determine pregnancy.
As we will discuss later, hCG can occasionally be produced by other cells within the body. However, in 99% of cases, elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin in a woman’s blood indicate pregnancy.
The hCG blood test is the most precise method for diagnosing pregnancy. When conducted at the appropriate time and interpreted accurately, it boasts a near 100% accuracy rate.
In recent years, home pregnancy tests have become increasingly available due to the ability to measure hCG levels in urine. However, urine tests are not as reliable as blood tests, and false-negative results may occur if the test is taken too early in the pregnancy.
How is hCG produced?
Human chorionic gonadotropin, an essential hormone for maintaining and developing a pregnancy, is generated by the trophoblast — a group of embryonic cells that eventually give rise to the placenta.
Roughly six days after the sperm fertilizes the egg, the developing embryo reaches the uterine wall and implants itself. From this point forward, the hCG hormone produced by the trophoblast enters the mother’s bloodstream, making detection possible through ultra-sensitive laboratory tests.
As the embryo and placenta continue to develop, an increasing amount of hCG is produced and released into the maternal circulation. In the early weeks of pregnancy, hCG levels double approximately every 2 to 3 days. If the rate of increase for human chorionic gonadotropin is unexpectedly low within the first 30 days of pregnancy, there may be something wrong with the pregnancy, such as fetal non-viability or an ectopic pregnancy.
When does hCG become detectable?
Current techniques can detect hCG from the 3rd or 4th week of pregnancy, counting from the date of the last menstruation.
As the 4th week of pregnancy typically aligns with the expected arrival of the next period, we recommend patients wait for a missed period before taking the test. This approach minimizes the risk of false-negative results.
hCG levels by the week of pregnancy
Generally, hCG levels behave as follows throughout pregnancy weeks:
- Non-pregnant women or under 3 weeks pregnant: less than 5 mIU/ml.
- 3 weeks pregnant: between 5 and 50 mIU/ml.
- 4 weeks pregnant: between 5 and 426 mIU/ml.
- 5 weeks pregnant: between 18 and 7,340 mIU/ml.
- 6 weeks pregnant: between 1,080 and 56,500 mIU/ml.
- 7 to 8 weeks pregnant: between 7,650 and 229,000 mIU/ml.
- 9 to 12 weeks pregnant: between 25,700 and 288,000 mIU/ml.
- 13 to 16 weeks pregnant: between 13,300 and 254,000 mIU/ml.
- 17 to 24 weeks pregnant: between 4,060 and 165,400 mIU/ml.
- 25 to 40 weeks pregnant: between 3,640 and 117,000 mIU/ml.
Note that the values above are for guidance only. Normal value ranges may vary among different laboratories.
If your hCG level differs, don’t worry, as it doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem with your pregnancy. The most crucial factor is the hormone’s growth rate during the early weeks.
hCG levels in multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets, are usually higher since more embryos mean more sources of chorionic gonadotropin production.
Typically, hCG peaks around the 10th week of pregnancy. Levels then decline until week 20, when they stabilize and remain relatively constant until delivery day.
Can hCG determine gestational age?
No, hCG levels serve only to diagnose pregnancy. Accurately estimating gestational age based solely on human chorionic gonadotropin levels is impossible.
If you examine the reference values provided earlier, you will notice significant variations in human chorionic gonadotropin levels throughout pregnancy weeks. For example, a woman in her 8th week of pregnancy may have an hCG level of 9,000, while another woman with the same gestational age may already have an hCG level of 150,000.
What is the difference between Beta-hCG and hCG?
hCG is a hormone composed of two large molecules called Alpha subunit (or Alpha fraction) and Beta subunit (or Beta fraction). The former is structurally similar to other hormones, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or luteinizing hormone (LH). The latter is unique, as it is not present in any other hormone.
The hCG produced by the fetus enters the mother’s bloodstream and undergoes a process of metabolism and degradation in tissues, liver and kidneys. This process generates several different hCG isoforms in the blood and urine, such as:
- Free beta-subunit.
- Free alpha-subunit.
- Nicked hCG.
- Nicked Beta-hCG
- hCG beta-subunit core fragment.
Blood pregnancy tests can measure intact hCG, Beta-hCG, or “total hCG,” which includes all hCG isoforms.
The term Beta-hCG (bHCG or β-hCG) has become popular over time as a synonym for a pregnancy test. However, it does not necessarily indicate that the test measures only the Beta subunit of hCG. Often, the test is called Beta-hCG, but the laboratory analyzes more than one isoform of the hormone.
Although they are not exactly the same, the terms Beta-hCG and hCG are often used interchangeably. Throughout our text, all information will be valid for both pregnancy tests called Beta-hCG or hCG.
Methods of measuring hCG
hCG is produced in the placenta, released into the mother’s blood, metabolized in the liver, filtered by the mother’s kidneys, and eliminated through urine. Therefore, hCG and its isoforms can be measured in both blood and urine of pregnant women. Except for rare cases, which will be explained later, if hCG is detected in a woman’s blood or urine, it means she is pregnant.
There are essentially two ways to assess the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin: qualitative hCG and quantitative hCG.
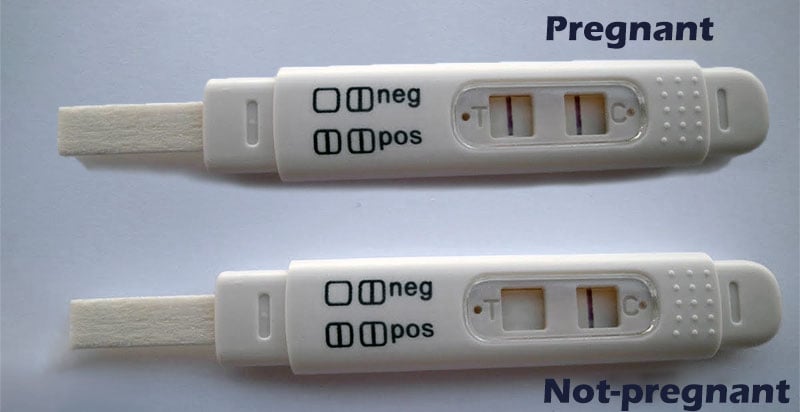
Qualitative hCG does not provide specific values; it only reveals whether or not significant levels of human chorionic gonadotropin are circulating in the mother’s blood. This method is widely used in over-the-counter pregnancy tests that use urine as the sample source.
These tests have a strip that reacts to the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin. The strip does not quantify the hormone; it only indicates whether it is present or not (the test is either positive or negative).
Quantitative hCG, on the other hand, is the method used in most blood tests. In this type of analysis, the result is given in values, typically in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/ml). Most laboratories consider a pregnancy to be underway when values exceed 25 mIU/ml.
How to interpret values (quantitative results)
It’s important to note that urine pregnancy tests are not used to establish a definitive pregnancy diagnosis. Even when they are positive, the result must be confirmed through a blood test, which is the most reliable pregnancy test.
Most blood tests can detect minimum hCG levels of 5 mIU/ml, but there are now supersensitive tests that detect the presence of as low as 1 or 2 mIU/ml.
The majority of laboratories use the following reference values:
- hCG below 5 mIU/ml: negative result, no ongoing pregnancy.
- hCG between 5 and 25 mIU/ml: inconclusive result, generally indicating no ongoing pregnancy, but it could be the case of a very recent pregnancy when there hasn’t been enough time for hCG to be produced in sufficient quantities to be detected in the blood. In these cases, the test should be repeated after three days.
- hCG above 25 mIU/ml: positive result, indicating an ongoing pregnancy.
It is always important to pay attention to the laboratory’s reference values. In most cases, laboratories use a value of 25 mIU/ml as the threshold. However, depending on the chemical method used, the value considered positive may be lower or higher.
Typically, for the embryo to implant in the uterus and for its hCG to reach significant levels in the pregnant woman’s bloodstream, it takes between 7 and 14 days after sexual intercourse.
In general, we only recommend taking the hCG test after a missed menstrual period because, before that, it is unlikely there has been enough time for hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in tests.
False-negative hCG results
False negative hCG results mainly occur when the test is taken too early. Some women might feel anxious after having unprotected sex and end up taking a pregnancy test just a few days later, even before experiencing any delay in menstruation.
Taking the test so soon is not helpful because, if you are pregnant, the embryo may not have reached the uterus yet. Without implantation in the uterus, hCG cannot be present in the mother’s bloodstream.
The latest generation of hCG tests can detect increased hCG levels with only a 1-day menstrual delay. However, to minimize the risk of false negatives, we recommend waiting at least a week after the missed period to take the test.
It is important to note that pregnancy cannot be entirely ruled out if a negative result is obtained within a week of a missed period. However, a negative result after more than two weeks of delay makes pregnancy highly unlikely.
For women with irregular menstrual cycles, determining whether their period is delayed may not be straightforward. In such cases, we recommend waiting 14 days after unprotected sex before taking the test.
Since the concentration of hCG in urine is lower than in blood, the risk of false-negatives is higher with urine tests.
Finally, medications, including traditional contraceptives, the morning-after pill, antidepressants, and antibiotics, do not cause false negatives. Infections also do not affect the result.
False-positive hCG results
With current hCG detection techniques, false-positives are rare. However, there are some situations where a false-positive result may occur:
One such case involves fetal death shortly after embryo implantation in the uterus. In this situation, the hCG can be positive, but since a miscarriage has occurred, there will be no pregnancy development. Early miscarriages might go unnoticed because the embryo is still microscopic.
Additionally, some women undergoing fertility treatments might use hCG-based medications. In these cases, the detected hCG in tests could merely be a remnant of the medication taken days earlier. Generally, after two weeks of discontinuation, this residual hCG will be eliminated and will no longer interfere with pregnancy tests.
Other medications don’t cause false positive hCG results, including contraceptives, the morning-after pill, antidepressants, antibiotics, clomiphene, or any other hormone.
In rare cases, patients who have recently had mononucleosis may experience false positive hCG results (with low values).
In older women nearing menopause, the pituitary gland in the brain may begin to secrete small amounts of hCG, enough to maintain levels just above 25 mIU/ml, although values between 7 and 15 mIU/ml are more common.
hCG-Producing Tumors
Some tumors produce human chorionic gonadotropin, as in gestational trophoblastic disease, which encompasses the following conditions:
- Hydatidiform mole (partial or complete).
- Invasive mole.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Placental site trophoblastic tumor.
These diseases produce tumors derived from the abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic cells. The production of hCG by these trophoblastic tumors can be quite significant, often exceeding 100,000 mIU/ml, and in some cases, reaching over 500,000 mIU/ml.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can hCG be detected in men?
Although rare, men can have detectable levels of hCG in cases of some types of cancer, such as testicular cancer. In healthy men, hCG levels should be below 2.0 mIU/ml.
Is it possible to be pregnant and receive a negative result from a blood test?
This can only occur if the test is performed too early, before the embryo has started producing hCG.
Can the hCG test be positive without being pregnant?
Yes, but this typically occurs in cases of tumors that produce the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin or in patients using infertility medication containing hCG.
How is the Beta hCG test performed?
The test is simple and carried out through a blood draw.
My hCG level is 25 mIU/ml; what does this mean?
A level of 25 mIU/ml is the cutoff value for pregnancy. This result usually indicates pregnancy in women of childbearing age, but it’s best to repeat the test after 72 hours. If the patient is indeed pregnant, the value should double within three days.
When does hCG production begin?
hCG production commences once the embryo implants in the uterus, an event that occurs about seven days after conception.
Can I estimate my gestational age using hCG levels?
hCG is an unreliable method for estimating pregnancy duration. It can determine if the pregnancy is very recent or not, but calculating the exact week of gestation is not possible.
Is fasting necessary before taking the Beta-hCG test?
No, fasting is not required.
References
- Hormonal evaluation of early pregnancy – American Society for the Study of Sterility & American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
- HCG Tumor Marker – American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC).
- Immunoassay of human chorionic gonadotropin, its free subunits, and metabolites – Clinical Chemistry.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin: The Pregnancy Hormone and More – International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
- Pregnancy tests: a review – Human Reproduction.
- Pregnancy Diagnosis – Medscape.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin: Testing in pregnancy and gestational trophoblastic disease and causes of low persistent levels – UpToDate.
- Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005.
Author(s)
Pedro Pinheiro holds a medical degree from the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and is a specialist in Internal Medicine and Nephrology, certified by the State University of Rio de Janeiro (UERJ) and the Brazilian Society of Nephrology (SBN). He is currently based in Lisbon, Portugal, with his credentials recognized by the University of Porto and the Portuguese Nephrology Specialty College.







Leave a Comment